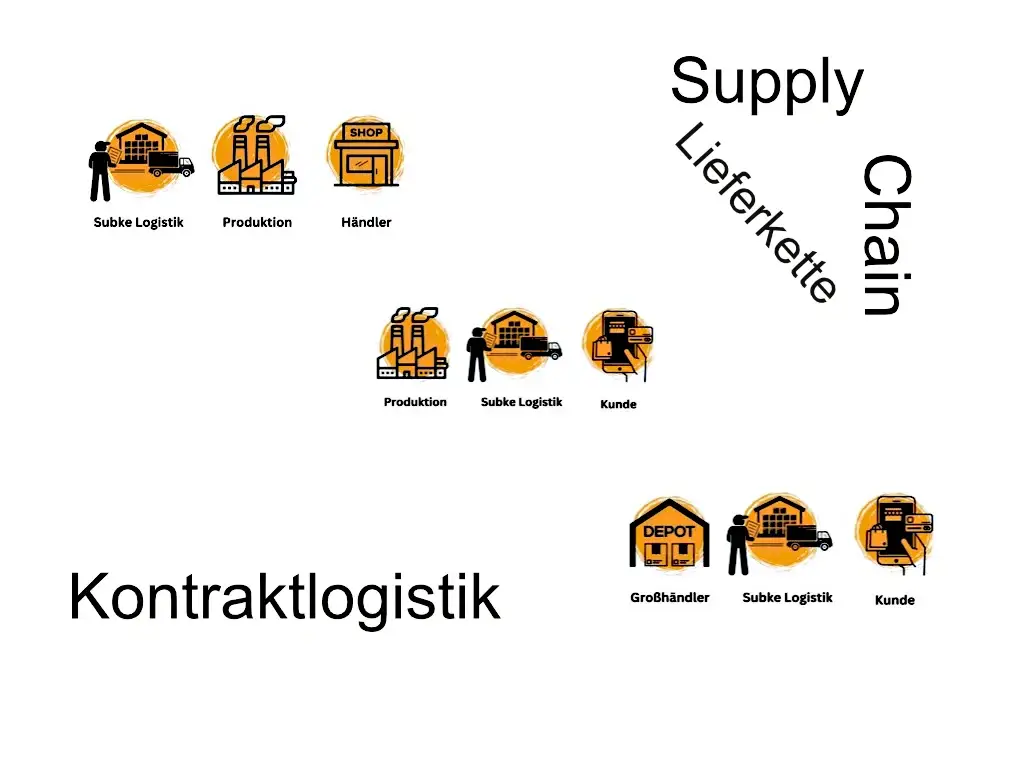
Contract logistics in supply chain management
Contract logistics comprises individual business models along thevalue chain as part of supply chain management, which is based on long-term cooperation between a manufacturer or retailer of goods and a logistics service provider based on the division of labor.
Cooperation between several parties (party logistics) is governed by a service agreement(contract), which covers the services with business volume and is individually structured.
Contract logistics plays a crucial role in a globalized economy in which the manufacturing industry in many sectors relies on a smooth and efficientsupply chain.
What is contract logistics?
Contract logistics, also known as third-party logistics(3PL), is an outsourcing model in which companies transfer all or part of their logistics activities to external service providers.
- Party – Production/Procurement
- Party – Warehouse/Fulfillment
- Party – Transportation
These service providers, often specializedcontract logistics companies, take over various aspects of the supply chain, including warehousing, transportation, distribution, inventory management and handling the entire order fulfillment process.
The contract logistics service provider not only takes on basic logistics services such as transportation, handling or warehousing(TUL), but also other logistics functions with increased complexity and problem-solving capabilities. These include, for example:
What is procurement logistics?
Procurement logistics ensures that a company, such as a manufacturer or retailer, receives the required materials, products or services in the right quantity, quality and at the right time to meet its operational requirements.
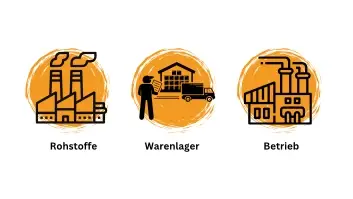
Procurement logistics comprises various tasks and activities, including
1) Supplier management: The selection, evaluation and maintenance of supplier relationships to ensure that reliable and high-quality deliveries are guaranteed.
2) Requirements planning: The determination of material or product requirements based on sales forecasts, stock levels and other factors.
3) Order processing: Creating purchase orders, communicating with suppliers and tracking deliveries to ensure that orders arrive on time and in the correct quantity.
4) Warehousing: The management of stock levels to ensure that sufficient materials are available without incurring unnecessary storage costs.
5) Transport and shipping: The planning and organization of the transport of procured goods from the supplier to the warehouse or production site.
6) Quality control: The monitoring and testing of delivered materials or products to ensure that they meet quality standards.
7) Cost optimization: The search for ways to reduce procurement costs, be it through negotiations with suppliers, better transport routes or more efficient warehousing.
What is production logistics?
This involves the procurement of goods and raw materials for the processing industry for the manufacture of end products. Optimized processes help to minimize production costs, shorten throughput times and improve product quality.
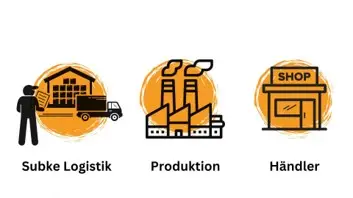
Production logistics comprises the following activities and tasks:
1) Material flow planning: This involves the planning and design of material flows within the production facility to ensure that materials and components reach the workstations efficiently.
2) Inventory management: The management of stock levels in the receiving warehouse of raw materials, semi-finished products and finished goods to ensure that production is not affected by material shortages or overstocks.
3) Just-in-Time (JIT) production: The implementation of JIT principles where materials are delivered exactly when they are needed to reduce storage costs and minimize waste.
4) Production planning and control: The creation of production plans, the allocation of resources and the monitoring of production to ensure that production targets are met.
5) Transportation and material movement: The organization of the movement of materials within the production facility, whether by conveyor belts, forklifts or other means.
6) Quality control: The monitoring of product quality during the production process to ensure that quality standards are met.
7) Resource planning: This involves the planning and coordination of labor, machinery and other resources to ensure that production runs smoothly.
The timely procurement of materials, individual or spare parts plays a decisive role in production logistics.
Call-off and material flow can vary greatly. Starting with the constant monthly sales volume, regular seasonal fluctuations and unexpected economic fluctuations, the basic requirements of the stock quantity must be available.
However, without having too much safety stock in the warehouse in order to keep storage costs as low as possible.
What is distribution logistics?
Within contract logistics, distribution takes over the distribution of goods from the manufacturer or supplier to the end customer or point of sale.
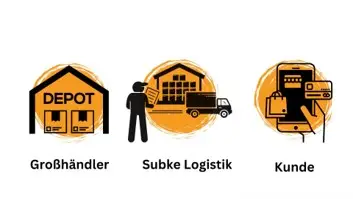
1) Warehousing and inventory management: The management of stocks in outgoing warehouses or points of sale. Good demand planning ensures that sufficient products are available to meet demand without incurring excessive storage costs.
2) Transport and shipping: Planning and organization of transport by CEP service providers or freight forwarders. Movement of goods from production sites or warehouses to distribution centers, retail stores or end customers. This can be done using various means of transportation such as trucks, ships, airplanes or railroads.
3) Route planning and optimization: Planning efficient transport routes to minimize delivery costs and shorten delivery times.
4) Warehouse locations and network design: The strategic selection of warehouse locations to optimize the reach and efficiency of the distribution network.
5) Order processing: Processing customer orders, picking products, packing and preparing them for dispatch.
6) Returns management: The processing of returns and returns from customers as well as the monitoring and management of defective or damaged products.
7) Customer service and communication: Providing information to customers about delivery status, tracking deliveries and resolving problems or complaints.
Distribution logistics is crucial to a company’s success, especially in sectors such as retail and e-commerce.
What is reverse logistics?
Reverse logistics refers to the return of goods. It takes over the process of managing and controlling flows of goods that move against the normal supply chain.
In other words, it is the return of products from the end consumer or point of sale back to the manufacturer or other participants in the supply chain. Reverse logistics includes activities such as returns, recycling, repairs, reprocessing and disposal of products and materials.
Here are some of the most important points of reverse logistics:
1) Returns: This is one of the most common use cases for reverse logistics. In fulfillment, products that are returned by customers must be properly processed, checked and a decision made as to whether they can be put back on sale or whether they must be taken back or reconditioned due to defects or other reasons.
2) Recycling: The recycling of products and materials is an important aspect of reverse logistics, especially in industries where recycling is an important environmental aspect. Examples include electronics, packaging and the automotive industry.
3) Repairs and maintenance: In some cases, products require maintenance or repairs, and reverse logistics includes the organization of the transport of these products to the repair shop and the return of the repaired products to the customer.
4) Reconditioning and resale: Some products can be resold after a thorough inspection and refurbishment. This can be a lucrative business opportunity in some cases.
5) Disposal: Products that cannot be reused, recycled or repaired must be disposed of properly. Reverse logistics involves the disposal of products in accordance with environmentally friendly standards and regulations.
Advantages of outsourcing contract logistics
Advantages of contract logistics:
1) Cost efficiency: Working with experienced logistics service providers enables companies to take advantage of economies of scale ➚ and reduce costs by optimizing logistics processes.
2) Focus on core competencies: Companies can concentrate on their main areas of business as they no longer have to worry about complex logistics tasks.
3) Resource savings: By outsourcing logistics, companies can reduce their own resources, such as warehouses and employees, and optimize the amount of capital tied up.
4) Storage space: You can use large storage areas for pallets, large containers and shelving racks for small items as required.
5) Goods management: With sufficient staff, a large number of pallets and containers can be stored and dispatched quickly.
6) Use expertise: Contract logistics service providers and their employees often have specialized knowledge and modern technologies to make processes more efficient.
7) Flexibility: Contract logistics enables companies to adjust their capacities according to demand, which is particularly advantageous in seasonal business.
Frequent challenges in contract logistics that companies have to overcome
Contract logistics, like any other form of logistics, comes with its own challenges. These include the complexity of supply chain management, fluctuations in demand, uncertainties in transportation, inventory management and much more.
While brick-and-mortar retailers generally manage logistics with their own “knowhow”, the use of logistics service providers at the physical goods distribution stages plays a greater role for sectors, particularly in e-commerce.
It is important to recognize these challenges and develop suitable solution strategies to ensure efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Challenges of contract logistics:
1) Dependence on third parties: Outsourcing logistics activities means that companies are dependent on the performance of their service providers, which entails risks. Service providers should have a certain number of their own employees and sufficient storage space.
2) Communication management: Effective communication between companies and logistics service providers is crucial to avoid problems. Communication should be as direct and fast as possible.
3) Data and information exchange: A smooth flow of information is crucial to ensure efficient collaboration. This is why most logistics service providers have a wide range of API interfaces that enable bidirectional data exchange in real time.
4) Safety and liability: Companies must ensure that their logistics partners comply with the required safety standards and can be held liable in the event of damage or loss. You should have public liability insurance. The retailer must notify his contents insurance company of the warehouse with the stored goods as an external warehouse.
Technology and innovation in contract logistics
Contract logistics is increasingly influenced by technology and innovation. Companies use modern logistics solutions such as track-and-trace systems, automated warehouse management systems, real-time data analysis and much more.
What is a track and trace system?
This is the active tracking of parcels. The consignment is given a unique number. This number can be used to determine the status and position of the parcel with the respective shipping service provider.
These technologies enable procurement logistics, intralogistics and transport logistics processes to be optimized, efficiency to be increased and better decisions to be made on the basis of real-time data.
What are automated warehouse management systems?
Modern robot technology (AGV) forms the core of partially or fully automated warehousing. They are able to take over the entire picking process 24/7. This means that many orders with a large number of items can be packed and shipped. The unit costs of items can be reduced within warehouse logistics with automation.
Which warehouse management software is offered?
Keeping an overview is essential for optimized warehouse processes. This requires sophisticated software with integrated real-time data analysis (real-time analytics). Well-known providers of warehouse management software are:
- Megaventory – SMEs and large companies
- SAP (WMS)- large retailers and large companies
- Easy WMS – large retailers and production
- JTL (WMS) – e-commerce and SMEs
- Cin7 – E-Commerce and SMEs
The tasks of warehouse management software are to record storage capacities, transport movements and inventory management with goods receipt, goods issue, stock transfer, settings for the initial quantities of items and inventory counting.
The software should also be able to manage price lists and article master data records with serial and batch numbers. Have a digital packing table and be able to create inventory reports.
Best practices in contract logistics:
1) Clear contracts: Carefully drafted contracts are critical to establish the responsibilities of both parties and clarify expectations.
2) Performance monitoring: Regular monitoring of logistics performance helps to identify and address problems at an early stage.
3) Use of technology: The integration of logistics software and systems can increase efficiency and facilitate the exchange of information.
4) Risk management: Companies should protect themselves against potential risks and consider taking out appropriate insurance.
Conclusion: The future of contract logistics
Overall, contract logistics offers companies the opportunity to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs and increase their competitiveness. However, it requires careful planning, clear communication and the selection of trustworthy partners to achieve the best results.
Most of the retailers believe that contract logistics will continue to be an important part of the value chain in the future.
It’s important to consider the individual needs of your business and work out the right strategy for your logistics, whether that means outsourcing individual tasks or the entire supply chain.
Contract logistics explained in the video